Understanding OEE
As you know, ever rising competition in the market for energy raw materials required for power generation has led to an increasing number of measures being undertaken in the mining industry to reduce the unit cost of production. One of the fields that offer considerable savings in this regard is the utilization of the technical resources owned by mines.
Productivity and efficiency of mining equipment are among the most important elements contributing to unit mining cost; and measuring and benchmarking them is one of the best ways of identifying losses and understanding the possibilities of improvement. One method to improve productivity is to utilize common equipment as efficiently as possible; thus, the correct estimate of equipment effectiveness is very crucial so that it can be upgraded.
Mining being a very capital-intensive industry aims to get early return on investments as well as reduced overall production cost. It is in this context that the blog discusses the notion of deploying a powerful metric called overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and main components of OEE – availability, utilization, and production efficiency.
OEE Calculation
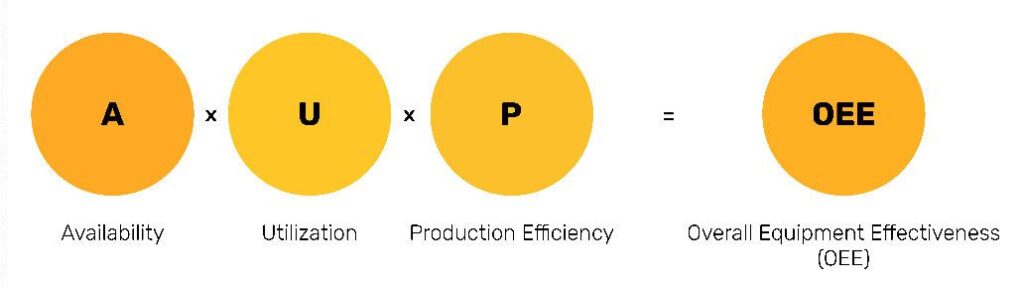
The widely accepted formula is calculated by multiplying availability, utilization and production efficiency. It is represented by a percentage.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness = Availability × Utilization × Production Efficiency
Overall Efficiency of Mining Equipment
Productivity of equipment can only be enhanced and controlled successfully if a precise performance measurement system is applied. Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a well-known method to measure performance of production equipment in manufacturing industries and nowadays has been adapted for the mining sector. Its main objective is to identify the roots of unproductive time losses for all operations inside the system that impact availability, utilization, performance, and quality.
Poor equipment efficiency in mechanized mining endangers the success of the mining operation. OEE improvement initiative triggers an improvement in almost all sections of the mine. In fact, OEE is a golden standard which serves as a continuous enhancement tool to unleash the true potential. Simply put, overall equipment effectiveness indicates how good the equipment is being used and is like a performance review for assets. OEE is the key performance indicators of equipment, and this is a universally accepted tool for decision making by mine management team.
Availability of a Mining Equipment (A)
Availability can be defined as the net time the machine is available to work divided by the total possible available time or planned production time. This metric does not include any performance numbers relative to how the machine operates while it is running. Availability takes into consideration “lost time” which includes any event that stop planned production for a long duration of time. This generally considers unplanned stops like equipment breakdowns, technical failures or material shortages and planned stops like frequent tool change-over or daily cleaning, etc. Availability (A) of machinery can be represented by the total number of hours the machinery is free from any event of maintenance or breakdown. It represents the period for which the machine is available for running.

Utilization of a Mining Equipment (U)
Utilization (U) denotes the use of available hours for actual working in the field. Due to inordinate idling conditions, a machine may be available but still may not be working in all the available hours. Thus, utilization signifies a loss in available hours. Equipment utilization, sometimes referred to as asset utilization, is a measurement of the use and performance of site machinery, which assists mining businesses to improve job-site productivity and reduce the cost of equipment rental and project delays.
Measuring Equipment Utilization: The important metrics that are used include ignition on/off times, engine hours, fuel use, high-definition GPS-based location, sensor data such as weight scales and PTO use, as well as engagement of machine parts. Understanding an asset’s location, how long its engine has been running and whether core machine functions have been used builds a picture of utilization that can be measured. Utilization is the proportion of time the equipment is available that it is used for its planned purpose.

Utilization is more effective in capacity planning and analyzing the absorption of fixed costs as availability considers the machine itself and focuses more on variable cost absorption. By increasing the utilization of equipment, one can help prevent worksite delays and minimize unnecessary equipment rental costs. One of the largest reasons for underutilization is equipment hoarding where machines sit idle on sites. Having visibility of assets that are not being used and where these assets are located, can go a long way to improve utilization.
Production Efficiency of a Mining Equipment (P)
Production Efficiency is the ratio of actual output from a machine to its rated output during the time that it is operating.

Poor reliability, while having some impact on equipment availability, is expected to have a bigger impact on production efficiency, due to the inefficiencies associated with starting up and shutting down equipment, and the time and effort that it requires to get the production operation back to a steady state situation.
It is reasonable that the costs of poor reliability generally show up in lower production efficiency. This is a measure that is often not given the same emphasis as availability or utilization measures, and in any case is generally considered to be a production responsibility, with the impact of maintenance on this figure generally going unnoticed.
Equipment running with slower speed and lesser capacity compared to the rated capacity led to poor production efficiency (e.g., if the trucks run slower and carry lesser tons of material than its actual capacity it will lead to poor production efficiency). Speed control and proper Payload monitoring system can alleviate this issue. Operator’s skills also play a key role here. Defects in quality and rework due to quality issue negatively impacts production efficiency. Inaccurate drilling, poor quality of blast, inaccurate digging, poor grade control plan led to increased rework, additional material movement and decreased production efficiency.
